In this section, we will define communication and discuss the components of the communication process.
1.1.1: Definition of Communication
In this text, we define communication as symbol using and meaning making. Communicators exchange two types of symbols, verbal and/or nonverbal, and attach meaning to said symbols. For example, the meaning attached to the verbal symbol “hello” is a greeting. You can also convey this greeting by using a nonverbal symbol, such as a hand wave. However, it is important note that the meanings we attach to symbols can vary from person to person. For example, another communicator might instead interpret a hand wave as trying to get their attention.
1.1.2: The Communication Process
In order to better understand how verbal and nonverbal symbols are produced, interpreted, and coordinated in interactions, it is necessary to understand the components of the communication process.
Senders and receivers of messages in a communicative interaction. Because we are continuously sending and receiving verbal and/or nonverbal messages, we are simultaneously both a sender and receiver in interactions. For example, in a face-to-face interaction, the other communicator may be recounting an experience verbally with words and nonverbally with hand gestures, while we are sending our own nonverbal messages via eye contact, facial expressions, posture, etc.
The process of turning our thoughts, ideas, and feelings into verbal and/or nonverbal messages.
The process of interpreting and adding meaning to the verbal and/or nonverbal messages we receive.
A thing that represents or stands for something else. In communication, symbols can be verbal, such as words, or nonverbal, such as the ‘okay’ hand symbol.
Verbal and nonverbal symbols that represent thoughts, feelings, and ideas. Messages can be both intentional (conscious) and unintentional (unconscious). For example, we may intentionally smile at a friend but unintentionally fidget with our hands when nervous.
The means through which the message is sent from one communicator to the other, such spoken words, a text message, or our hands to make a gesture.
The verbal and nonverbal messages sent by one communicator in response to the other communicator’s message(s). For example, if someone says a word we are unfamiliar with, we may frown in response or give them a confused look to let them know we do not understand.
Noise is a type of interference in the communication process that results from the physical, relational, individual, and/or cultural context. Noise can occur in various places in the process, such as in the people, in the channel, in the message, and even outside the interaction.
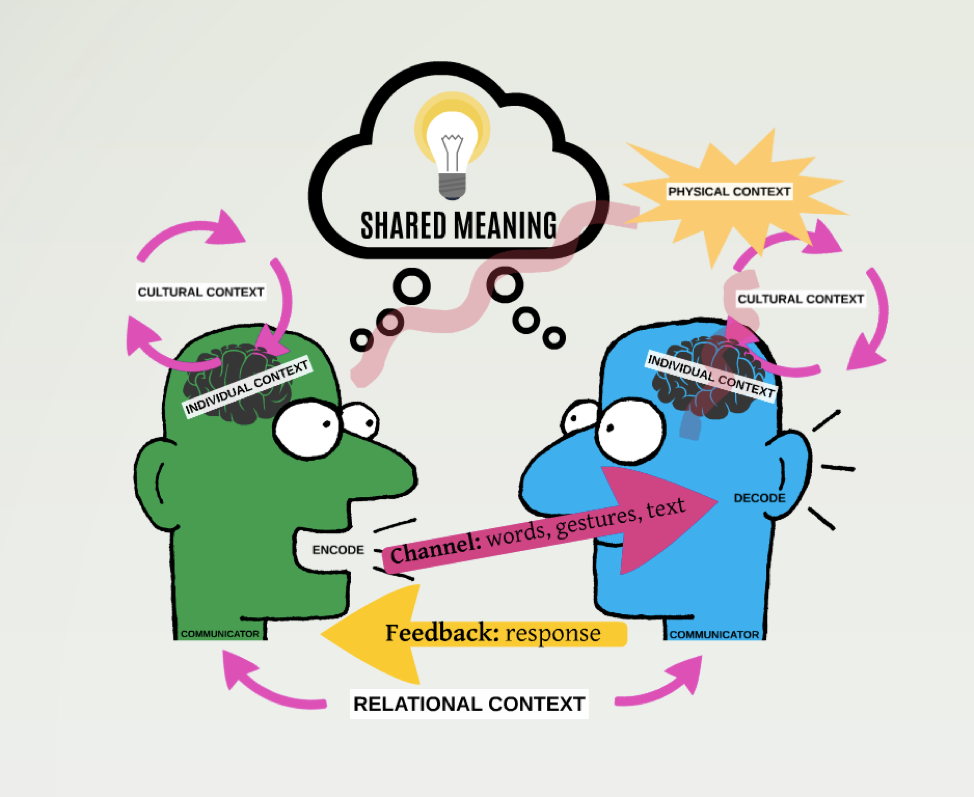
(Image: The Communication Model. Pamela J. Gerber, CC BY NC SA 4.0)
In any interpersonal interaction, there are at least two communicators and both communicators are generating and creating meaning by simultaneously sending and receiving messages. For example, in a face-to-face interaction, we may be telling a story about our horrible day and the other person may be listening. While we are telling our story, we are encoding our thoughts and feelings and considering which details to leave out and which ones to talk about. Think about the last time you recapped your experience at a social gathering for a friend and then again for a family member. Did you focus on different details with each person? That’s encoding. While telling the story, we may use both verbal and nonverbal symbols to create the content of our message. The channel we send our message through can be spoken words (for verbal symbols) or hand gestures (for nonverbal symbols). The other communicator, who is listening, decodes the message by interpreting and adding meaning to it. In addition, the listener is also simultaneously communicating messages back to us. This is called feedback. They may be nonverbally establishing eye contact (or not), yawning, or verbally interrupting or asking questions.
