Part 5: Chapter 29
The following chapter contains sample argument and persuasion essays. The first essay below is not well-developed, and it was included in the textbook A Guide to Perspective Analysis to illustrate the contrast between writing that has undergone a revision process and writing that was slapped together at the last minute.
Those Misleading Manhattan Friends (Sample Essay)
Television. According to Webster’s New Collegiate Dictionary, television is a system for transmitting images and sound into a receiver. Television influences how we think. As part of the media, it shows us ways to consider the ways we see the world. In the show Friends three major contradictions can be found that can be seen by the discerning viewer. As this paper proceeds each of these contradictions will be made more clearer.
The first of these contradictions has to do with the economics of the major characters within the show Friends. Manhattan is an expensive place to live; it is expensive because the rents are high their. My friend lives in Manhattan. My friend pays a lot for rent in Manhattan. My friend pays over 2,000 dollars a month for a studio apartment in Manhattan. My friend has a good job in Manhattan and still has difficulty making ends meet in such an expensive city as Manhattan. Ross is a teacher. He teaches at the University. Ross lives in a nice apartment. Teachers make very little money. Even University teachers make very little money. Phoebe is a masseuse. She gets paid per job. She lives in a nice apartment. She makes 50 dollars per job. She is always at the coffee shop with her friends. How many jobs can she do in a week? Rents are just too high overall.
Another contradiction within the show Friends is their relationships. Ross and Rachel date each other. Ross and Rachel indubitably break up. This usually happens at the end of each season. They are still friends. I cannot be friends with anyone I break up with. My feckless girlfriend and I dated for six years. Then she changed 360 degrees into a different person. She broke my heart. I do not wish to talk to her anymore. Rachel and Ross have a kid together. There kid is very cute. They were once married to each other. They still get together and go two movies as if they simply have a causal relationship. This is a contradiction to. I think now Joey and Rachel are dating. I am sure that they will brake up to.
Another contradiction within the show Friends has to do with the modern, complex, ever-changing, technological, fast paced world that we live in today. Few people stay in one place anymore. People move a lot. Only 1 friend from my high school steal lives in the same area. Ross, Rachel, Joey, Chandler, Phoebe, and Monica never move. Except when they move in and out of each others apartments. They also never make gnu friends. Except when they date other people for about half a season and then get bored and come back and end up dating each other again.
In conclusion, Friends is full of mini and varied contradictions. It is knot a very realistic show. For one, the characters live in Manhattan and they would not be able to afford to live their especially Ross and Phoebe. For two they date each other and have kids together and the brake up but they still remain friends. And for three and finally they never move or make new friends in eleven years!!! Yet the show is popular. I suppose there are many reasons why it is popular.
This essay took less than an hour to write. I started with an outline for each of the five paragraphs and followed it precisely and quickly, throwing in the main ideas without further thought, revision, or editing (okay, I did challenge myself to include several common misspellings that spell check would not catch). Even still the piece is not completely hopeless. The notion that a show like Friends can lead audiences to accept false impressions of reality could have proven intriguing to explore, and if this essay were not written by me as a parody but by a student in earnest, I would try to help the student focus the paper around this theme and further develop relevant ideas.
When you respond to the writing of your peers, keep in mind that we all have to write drafts and that it is always better to focus on the positive, for example, how the writing could become more effective, rather than the negative, and explicating what is wrong with it at the moment. In fact, when running writing workshops, I insist that all the feedback be stated in terms of what we like (so the writer knows what to keep or expand in subsequent drafts) and how it can be improved (so the writer has specific advice as to how to make the essay better). This helps writers get excited about the potential of their essays rather than depressed about their current shortcomings. Ultimately it’s our attitude about our writing that causes us either to give up on it entirely or to continue to improve it.
Ultimately it’s our attitude about our writing that causes us either to give up on it entirely or to continue to try to improve it.
¶
The difference between the previous essay on Friends and the following one that I wrote on a strange museum in Los Angeles did not emerge from the potential interest of the subject matter but from the time and effort that I put into the writing of each. The piece that follows took several days and many drafts as I integrated experience, research, and critical examination to develop my analysis. When writing it, I used the advice I’ve given you throughout this book, so for the sake of review, I will explain how I created it before providing you with the finished draft.

When I first visited The Museum of Jurassic Technology I was dumbfounded by what awaited me inside the building. Stumbling through the dark building, I discovered a series of dioramas on such odd and diverse subjects as spores that take over the brains of ants, bats whose radars can pierce through lead, artifacts found in American trailer parks, illustrations of archaic beliefs and superstitions, and a convoluted and bizarre theory of how memory functions by a man I’d never heard of named Geoffrey Sonneabend. Later, when I discovered that parts of the collection were made up (including both Sonneabend and his theory of memory) and other parts were simply unremarkable, I felt the need to write about the experience in my journal:
How could I have been so stupid? “Museum of Jurassic Technology?” There was no technology in the Jurassic period, just a bunch of dinosaurs stomping around. I let the word museum lead me to think that the rest of the title made sense. And I should have realized when I entered that the items in the collection have nothing in common with each other, have no remarkable characteristics, are scientifically impossible, or just don’t make any sense. I consider myself a critical thinker but maybe I’m just as conditioned as everyone else to accept institutional authority.
As I reflected further on the significance of my visit, I decided that the museum is not the only place where questionable information gets passed off as objective and factual. In school, teachers often ask students to simply repeat information and seldom encourage them to critically examine it, a trend that has become even more common since standardized testing has dominated so much of the current curriculum. This emphasis on memorizing answers does not encourage us to think past the obvious, leading us to accept provisional theories as though they are universal truths. The museum makes us aware of this by using academic sounding phrases to get us to momentarily accept even the most ridiculous claims.
With this working thesis in mind, I set the stage for writing my essay. I researched the museum and related issues, evaluated each aspect of my visit in light of the Pentad, and brainstormed on the museum’s wider significance. I then collated and reviewed all of my observations and notes into a first draft, focusing mostly on developing this thesis. I then wrote a second draft in which I included stronger transitions and more deliberate opening and closing paragraphs. Then I produced a third draft, in which I tried to make the style more accurate and varied. I showed this draft to some of my colleagues who gave me excellent suggestions concerning other sources to consult, parts I should cut or develop, and organizational tips. After this, I submitted it to the online journal Americana where, after completing more revisions suggested by their editors, it was originally published. When reading it, think about the process that went into creating it, and how it didn’t spring out of the blue but developed slowly through careful consideration and deliberate revision.
The Museum of Jurassic Technology
Creating an essay like this takes time, but it is time well spent. Even if you never write another analytical essay after you finish school, the resulting mental stimulation will both enable and encourage you to think about your own life more deeply and help you discover ways to make it better. And analysis can also lead us to create a better world in general. Given the problems we face stemming from environmental damage, nuclear proliferation, and economic instability, we will need a massive amount of critical thinking spread throughout the entire world to insure our very survival. Because for many years I have studied just how creative and resourceful people can be, I believe we have the ability to solve these problems and live more fulfilling lives as we do so. This can only happen, however, when more of us take the time to slow down and analyze the world around us, so that we can add our perspectives to the written and spoken conversations that make up our culture, our history, and our lives.
Misinformation and Biases Infect Social Media, Both Intentionally and Accidentally
Giovanni Luca Ciampaglia and Filippo Menczer
Social media are among the primary sources of news in the U.S. and across the world. Yet users are exposed to content of questionable accuracy, including conspiracy theories, clickbait, hyperpartisan content, pseudo QXFAAAAEV and even fabricated “fake news” reports.
It’s not surprising that there’s so much disinformation published: Spam and online fraud are lucrative for criminals, and government and political propaganda yield both partisan and financial benefits. But the fact that low-credibility content spreads so quickly and easily suggests that people and the algorithms behind social media platforms are vulnerable to manipulation.
Explaining the tools developed at the Observatory on Social Media.
Our research has identified three types of bias that make the social media ecosystem vulnerable to both intentional and accidental misinformation. That is why our Observatory on Social Media at Indiana University is building tools to help people become aware of these biases and protect themselves from outside influences designed to exploit them.
Bias in the brain
Cognitive biases originate in the way the brain processes the information that every person encounters every day. The brain can deal with only a finite amount of information, and too many incoming stimuli can cause information overload. That in itself has serious implications for the quality of information on social media. We have found that steep competition for users’ limited attention means that some ideas go viral despite their low quality – even when people prefer to share high-quality content.
To avoid getting overwhelmed, the brain uses a number of tricks. These methods are usually effective, but may also become biases when applied in the wrong contexts.
One cognitive shortcut happens when a person is deciding whether to share a story that appears on their social media feed. People are very affected by the emotional connotations of a headline, even though that’s not a good indicator of an article’s accuracy. Much more important is who wrote the piece.
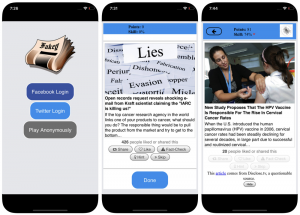
To counter this bias, and help people pay more attention to the source of a claim before sharing it, we developed Fakey, a mobile news literacy game (free on Android and iOS) simulating a typical social media news feed, with a mix of news articles from mainstream and low-credibility sources. Players get more points for sharing news from reliable sources and flagging suspicious content for fact-checking. In the process, they learn to recognize signals of source credibility, such as hyperpartisan claims and emotionally charged headlines.
Bias in society
Another source of bias comes from society. When people connect directly with their peers, the social biases that guide their selection of friends come to influence the information they see.
In fact, in our research we have found that it is possible to determine the political leanings of a Twitter user by simply looking at the partisan preferences of their friends. Our analysis of the structure of these partisan communication networks found social networks are particularly efficient at disseminating information – accurate or not – when they are closely tied together and disconnected from other parts of society.
The tendency to evaluate information more favorably if it comes from within their own social circles creates “echo chambers” that are ripe for manipulation, either consciously or unintentionally. This helps explain why so many online conversations devolve into “us versus them” confrontations.
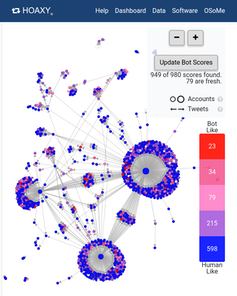
To study how the structure of online social networks makes users vulnerable to disinformation, we built Hoaxy, a system that tracks and visualizes the spread of content from low-credibility sources, and how it competes with fact-checking content. Our analysis of the data collected by Hoaxy during the 2016 U.S. presidential elections shows that Twitter accounts that shared misinformation were almost completely cut off from the corrections made by the fact-checkers.
When we drilled down on the misinformation-spreading accounts, we found a very dense core group of accounts retweeting each other almost exclusively – including several bots. The only times that fact-checking organizations were ever quoted or mentioned by the users in the misinformed group were when questioning their legitimacy or claiming the opposite of what they wrote.
Bias in the machine
The third group of biases arises directly from the algorithms used to determine what people see online. Both social media platforms and search engines employ them. These personalization technologies are designed to select only the most engaging and relevant content for each individual user. But in doing so, it may end up reinforcing the cognitive and social biases of users, thus making them even more vulnerable to manipulation.
For instance, the detailed advertising tools built into many social media platforms let disinformation campaigners exploit confirmation bias by tailoring messages to people who are already inclined to believe them.
Also, if a user often clicks on Facebook links from a particular news source, Facebook will tend to show that person more of that site’s content. This so-called “filter bubble” effect may isolate people from diverse perspectives, strengthening confirmation bias.
Our own research shows that social media platforms expose users to a less diverse set of sources than do non-social media sites like Wikipedia. Because this is at the level of a whole platform, not of a single user, we call this the homogeneity bias.
Another important ingredient of social media is information that is trending on the platform, according to what is getting the most clicks. We call this popularity bias, because we have found that an algorithm designed to promote popular content may negatively affect the overall quality of information on the platform. This also feeds into existing cognitive bias, reinforcing what appears to be popular irrespective of its quality.
All these algorithmic biases can be manipulated by social bots, computer programs that interact with humans through social media accounts. Most social bots, like Twitter’s Big Ben, are harmless. However, some conceal their real nature and are used for malicious intents, such as boosting disinformation or falsely creating the appearance of a grassroots movement, also called “astroturfing.” We found evidence of this type of manipulation in the run-up to the 2010 U.S. midterm election.
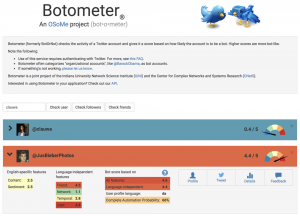
To study these manipulation strategies, we developed a tool to detect social bots called Botometer. Botometer uses machine learning to detect bot accounts, by inspecting thousands of different features of Twitter accounts, like the times of its posts, how often it tweets, and the accounts it follows and retweets. It is not perfect, but it has revealed that as many as 15 percent of Twitter accounts show signs of being bots.
Using Botometer in conjunction with Hoaxy, we analyzed the core of the misinformation network during the 2016 U.S. presidential campaign. We found many bots exploiting both the cognitive, confirmation and popularity biases of their victims and Twitter’s algorithmic biases.
These bots are able to construct filter bubbles around vulnerable users, feeding them false claims and misinformation. First, they can attract the attention of human users who support a particular candidate by tweeting that candidate’s hashtags or by mentioning and retweeting the person. Then the bots can amplify false claims smearing opponents by retweeting articles from low-credibility sources that match certain keywords. This activity also makes the algorithm highlight for other users false stories that are being shared widely.
Understanding complex vulnerabilities
Even as our research, and others’, shows how individuals, institutions and even entire societies can be manipulated on social media, there are many questions left to answer. It’s especially important to discover how these different biases interact with each other, potentially creating more complex vulnerabilities.
Tools like ours offer internet users more information about disinformation, and therefore some degree of protection from its harms. The solutions will not likely be only technological, though there will probably be some technical aspects to them. But they must take into account the cognitive and social aspects of the problem.
Editor’s note: This article was updated on Jan. 10, 2019, to replace a link to a study that had been retracted. The text of the article is still accurate, and remains unchanged.
____________________
Giovanni Luca Ciampaglia is an Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University of South Florida. Filippo Menczer is a
Professor of Computer Science and Informatics and the Director of the Center for Complex Networks and Systems Research at Indiana University. This article originally appeared in The Conversation.
Misinformation and Biases Infect Social Media, Both Intentionally and Accidentally by Giovanni Luca Ciampaglia and Filippo Menczer is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Does Recycling Actually Conserve or Preserve Things?
Samantha MacBride
There are a series of assumptions behind the familiar assertion that recycling saves resources and energy, and in so doing, protects the environment. These assumptions are in the motto, “recycling saves trees.” With recycling – one assumes – used materials stand in for raw materials. This way, recycled content cuts down on the need to extract (conservation), which in turn prevents some of the environmental damage from extraction that would be taking place without recycling (preservation).
Conservation and preservation are distinct, though linked, ideas. Historians of North American environmentalism distinguish the Conservation Movement, which focused on the responsible management of materials to sustain production and economic growth, from the Preservation Movement, which stressed the protection of wilderness.1 Both movements have been rightly critiqued for failing to consider questions of power and equity in people’s health, dignity, and livelihoods.2 Still, the distinction between conserving resources for use in production, and preserving complex ecosystems (which include people in human settlements), is useful for a question I now pose about recycling. Does recycling, in the way it is practiced today, actually conserve or preserve things that matter?
To answer “yes” requires that a set of assumptions hold true. When we say recycling saves trees, we start by assuming that the paper in the recycling bin goes to a plant to be sorted and baled. Plant managers find buyers for the bales, which are shipped off to a manufacturer. We assume that this manufacturer, individually or as part of a larger industry sector, is weighing the options between using virgin input (wood pulp) or secondary input (recycled paper). When it costs less to use recycled paper as an input, the manufacturer is going to use the secondary material to make things. So far, so good.
But to save trees, much less forests, more has to happen. When the decision is made to use recycled input, the virgin alternative ought to be conserved in a way that preserves ecosystems and people. Preservation isn’t achieved if the virgin stock is directed into a new product that hasn’t existed before; or if it is conserved technically for later use, and then harvested and utilized when economic growth makes for favorable conditions to ramp up production. It’s not enough to simply offer up recycled paper on a commodity market to be grabbed when price signals are favorable. It doesn’t do to merely measure increases in recycled content of various products on the market. Nor is it sufficient to theorize that recycling may have slowed a sectoral growth rate that would have proceeded, all things being equal, faster in an imaginary world in which there was no recycling at all. To save trees in a way that matters ecologically and socially means something more. It means that forests, including forest ecosystems and surrounding livelihoods in all of their complexity, are actually protected in today’s world.
Theoretically, there is no reason why recycling couldn’t deliver on such protection, were it integrated into a system of monitoring that followed through on promises. Such a system would need to identify limits on rates of extraction in accordance with their ecosystemic threat; include long term planning for stabilization of some extractive industries, and phase-out of others; and ensure maximum protection of future lands and ecosystems from development. Under such a system, extractive industries would need to demonstrate to what degree recycled inputs substituted for virgin sources in their sectors annually, and also that their sectors were not encroaching with new development in terrains that matter to people and other living things.
Empirically, there is no question that at certain times, for certain periods, recycling may have conserved virgin resources to some degree; and even that recycling may play a role in localized resource policies, such as boosting timber plantations that spare virgin forests as sources in papermaking. In fact, portions of the assumption of conservation, can be and regularly are dragged out for theoretical and/or empirical testing within the disciplines of resource economics, materials flow analysis, and life cycle analysis. There is much scholarship that asks whether recycling has resulted in, or could theoretically result in, less net extraction or harvest.3 Such inquiries are interesting in their own right, and to the extent that they tell us something about tradeoffs that manufacturers make between virgin and recycled inputs, they inform an understanding of what recycling could, under ideal circumstances, achieve in terms of actual conservation — which would be a precondition for, but not a guarantee of, actual preservation.
We are on shaky ground, however, if we take these assumptions for granted. I trace my concern on this matter to the work of William Stanley Jevons.4 In the 19th century, technological improvements in mining and combustion were greatly improving the efficiency of using coal as fuel. Noting these developments, Jevons argued that, rather than conserve coal, improvements in efficiency, and a subsequent drop in coal price, would paradoxically lead to an increased demand for coal.
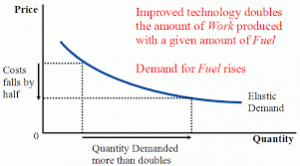
Now known as Jevons’ Paradox, this perspective observes that when you increase efficiency in production and consumption, you may well see an increase in overall extraction.5 Massive amounts of scholarship have followed the Jevons’ Paradox, most around energy efficiency.6 In the materials realm, recycling can be thought of as a form of efficiency (getting more out of the same input).7 There is a growing body of work tracing the effects of recycling on extraction of virgin materials, in particular in the area of metals.8 Scholars ask questions about conservation of metals in part because the data on their trade is more available than for other materials. It’s more organized. It’s more harmonized among different nations, given the nature of these economies. Both the economy of metals and as well as the material properties of metals make them relatively easy to be recycled over and over again and be reintroduced back into production, especially in comparison the heterogeneous range of synthetic polymers we call plastics. Yet we see growing rates of metals extraction taking place alongside growing recycling rates, worldwide. We can speculate about what those growth rates would have been had recycling not existed, but it would be hard to argue that global production systems are using less virgin raw material as a result of metals recycling, much less that metal recycling is preserving lands from mining.9

The caveats and careful measurements in the specialized literatures above suggest that recycling can conserve resources temporarily in some cases, almost always absent considerations of preservation. Such nuances fall away, however, as recycling becomes idealized and abstracted as an ethical, “earth-saving” end unto itself. Under-examined assumptions of conservation and preservation run deep through recycling discourse, and are also core to the notion that reuse will cut down on the flow of materials and energy from cradle to grave. Each time reuse and recycling are affirmed in the waste hierarchy, there is a hazy sense that somewhere, by someone, some sort of accounting is going on to ensure that overall, recycling is delivering protection of things that matter. I would wager that many in the media, in environmental education, and even in environmentally focused NGOs hold this position. This is how recycling would, actually and not just in theory, “save the planet.” But is there really any coordinating body who is conducting such accounting? No.10 And is recycling actually preserving ecosystems and livelihoods, or achieving real-world “dematerialization” (the technical term for less use of raw materials overall)? Not in any systematic way.11
Oil, Gas, and Plastics
So far I’ve used the examples of forest products and metals. I have done so because of the historical potency of the motto “recycling saves trees”, and the relatively developed scholarship around steel, aluminum, and other metals. In reality, much more is going on around forestry, or the mining and metals trade, than is taken into account when one simply looks at recycling. But at least we have some data to inform questions. If we examine the plastics industry and the role of plastics recycling, we find that similar assumptions abound, with particular complications, and little information. How can we evaluate the assumption that plastic recycling reduces the need to extract fossil fuels; or the separate but related claim that manufacturing with recycled inputs uses less energy, meaning lower fuel use economy-wide, meaning diminished carbon emissions?
It is well known that only a small percentage of global fossil fuel extraction is used directly in plastics production.12 So even recycling every shred of plastic would not, on its own, diminish the need to drill at current rates by much. Looking specifically at the U.S., the situation is no different. Let’s say we build up domestic plastic recycling capacity in the U.S., as many are calling for in the wake of China’s imports restrictions. What would the effect be of repatriating that tonnage, and feeding it back into domestic production, on domestic fossil fuel extraction – to make plastics, or to generate electricity?
It may surprise you to learn that the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) “is unable to determine the specific amounts or origin of the feedstocks that are actually used to manufacture plastics in the United States.”13
The reason hints at the constantly fluctuating conditions of virgin raw material sourcing that I’ve alluded to above, and data limitations that I’ll elaborate below. The EIA writes:
Because the petrochemical industry has a high degree of flexibility in the feedstock it consumes and because EIA does not collect detailed data on this aspect of industrial consumption, it is not possible for EIA to identify the actual amounts and origin of the materials used as inputs by industry to manufacture plastics. 14
Let’s pivot back to the day-to-day understanding of recycling, in which it is it is axiomatic to assert that plastic recycling saves oil and gas resources.15 On a ton-for-ton basis, in a hypothetical scenario in which recycled materials actually substitute for fossil fuels, and lead to a concomitant net decrease in extraction or fuel combustion, such claims hold. But without data on “actual amounts and origin of materials used as inputs,” it is not possible to evaluate the actual effect of plastics recycling on conserving such inputs. This would be the precondition to assessing what role, if any, plastics recycling has on actual preservation of things that matter in the U.S. (such as coastal communities, Indigenous peoples’ lands, and/or arctic wildlife refuges).
Frequent assumptions are being made among well-intentioned members of the media, environmental organizations, and concerned individuals that actual, current recycling efforts are part of real world protection. In more specialized discussions around Zero Waste and Circular Economy, there is a rolling process of coming to terms with hints that assumptions of conservation and preservation don’t hold. If, for example, we are dismayed to learn that plastics are “downcycled,” our dismay betrays a faith in the assumption of preservation in the background. If only plastic bottles could be produced in a closed-loop fashion, we reason, then we would be able to conserve at least some of the resources that would otherwise be extracted. Presumably, such conservation is needed for ecosystemic preservation, not just to boost the economic fortunes of the plastics industry.
Now let’s turn to the huge, multinational firms in the petrochemical industry that drill for the precursor materials for plastics at the beginning of the production chain. Let’s say more Americans recycled their plastics, and this resulted in an influx of more recycled plastic onto the market. Even with robust closed loops achieved, does anyone really think that the executives at one of these multinationals would get to the point of saying, “well, you know, it’s good that the need for input materials is being met by recycled plastic, and that means that this year we can scale back production a bit. We don’t need to open up a new offshore platform. It isn’t required to meet society’s needs after all!”
Ultimately, this would have to be the scenario in which more and more recycling of plastics actually preserved things that matter ecologically and socially. Yet very little of the empirical work needed to trace materials flows exists in the area of plastics recycling, in part because of a dearth of data.16 And in the area of plastics waste we have perhaps the most egregious misuse of claims that recycling is going to address problems related to pollution and climate change. The industry, and affiliated academic researchers, carry out life-cycle analyses that are impeccable in their methodological approach to quantifying different energy and material requirements associated with primary and secondary flows of plastics.17
None to my knowledge, however, answer the question of what more plastics recycling would do to diminish overall ecosystem withdrawals of fossil fuels. Does tar-sands extraction slow as a result? How about pipeline construction? Perhaps, with improved plastics recycling, we don’t need a Northeast U.S. expansion of storage capacity for hydrofractured natural gas. Not yet? Well, then, what are the plans for the scaleback?
Ideological Implications
These are both empirical and ideological questions. 18 They are ideological because a general optimism about recycling as earth-saving has become internalized in the thought processes of children and adults genuinely concerned about preservation. In everyday speak, assumptions of conservation and preservation swirl in a distant, misty background. In order to preserve optimism, can-doism, and a solutions oriented outlook it is easier not to look into these depths. In fact, critique of recycling’s earth-saving claims falls harshly on concerned ears, leaving bewilderment and a sense of betrayal. Sometimes, it is met with a binary response: either recycling is part of an overall process of saving resources and saving energy and by extension it’s saving the planet, or it’s a waste of time and it’s a sham and a lie.
I would urge all who are interested in this kind of thing to move away from binaries. The alternative is uncertain and less morally satisfying. It requires taking multiple perspectives, and wading through material complexity, power relations, institutional arrangements, and ideological maneuvering around recycling, asking again and again how, or even if, this or that initiative — often proudly and cheerfully announced by a consortium of producers — preserves things that matter. It also means looking at how recycling actually takes place in any particular place and time, not just under modelled conditions. Some of this work involves redirecting outrage. So, for example, if recycling plants are unable to sell recycled plastics because of market slumps, it is less morally shocking than a reflection of market conditions that they will landfill them instead? When people ask me about the crisis in North American plastics and paper recycling, which China’s trade policies has brought about, I’m tempted to respond, “what did you expect?” Recycling firms are tails wagged by massive dogs: neither evil, nor earth-saving, but actually a reflection of the organization of material exchange under the global market system, today.
In part, the potential for recycling to actually conserve and preserve is an empirical question, and the answers will vary from place to place and material to material. But it’s not just a matter of collecting data, or organizing the right technical systems. It also means recognizing that recycling as we know it may start with an ethical impulse, but materially translates into nothing more or less than a set of business practices. As with the 19th and early 20th scrap trades, recycling is part of smart industrial operations (nothing wrong with that). But let us dismantle the faith that recycling, as practiced currently, will save the earth if we do more of it. Affirming this ideal is a potent tool used by powerful networks of big producers, big extractors, and constellations of firms at the global level. Make no mistake, they are undertaking this strategy daily, with increasing sophistication. They understand the nuances of material sourcing, production volumes, input substitution, and property acquisition all too well. They rely on the fact that you don’t — and, in fact, can’t — because much of the data you would need for such an understanding is proprietary to them.
It is no easy feat to press producers to explain how recycling stands to scale back their operations, reduce their net output, or redress the ravages they have left behind. Such questions are typically outside the scope of a particular recycling project; easy to evade. As a group, these are smart folks. They know which NGOs to fund, which scholars to support, and where to make public appearances. They even understand the critiques that come out of discard studies, so they start to speak of “plasticity” instead of plastics; and they use the term“litter” to name the crisis of marine plastics.
But if you are in a position to do so, politely ask corporate spokespeople how the tonnage they take credit for recycling fed back into their operations last year, in a specific country, and how it in turn measurably reduced virgin extraction. Be specific. Ask them where and when it led to a reduced material throughput in their company or industry. Query them on the documented, not speculative, environmental protection afforded by, say, making cheap picture frames made out of spent polystyrene packaging. Reject the notion that cheap picture frames are a social good that would have needed to be manufactured with fracked natural gas, had polystyrene recycling not yielded up secondary inputs.
In the meantime, sit for a while to contemplate the fact that recycling, as it exists today, does not in fact save ecosystems in a way that matters on the whole ecologically or socially. How would recycling need to be practiced to achieve this desired end? In a different context of extraction, production, and growth – with different politics, knowledge structures, and ideologies. I realize this is an unsatisfying conclusion, but I believe in the importance of critique as a precondition to developing collaborative solutions. I have presented this information as part of a process of thinking through short-, medium- and long-term characteristics of this different context. This is an ongoing project to which I invite responses, as well as empirical contributions that would refine or refute what I have presented here.
Footnotes
- Hays, S. (1999). Conservation and the gospel of efficiency: The progressive conservation movement, 1890–1920. No. 40. University of Pittsburgh Press.
- See Guha,R. (YEAR). “Radical American environmentalism and wilderness preservation: a third world critique” Environmental Ethics 11, no. 1:71–83; Faber, D., and D. McCarthy. “Neo-liberalism, globalization and the struggle for ecological democracy: linking sustainability and environmental justice.” Just sustainabilities: Development in an unequal world (2003): 38-63.
- See Geyer, R. et. al. (2016) “Common Misconceptions about Recycling” Journal of Industrial Ecology 20, no. 5: 1010–17
- Jevons, W. S. (1866) The coal question: an inquiry concerning the progress of the nation, and the probable exhaustion of our coal-mines. London, UK: Macmillan and Company .
- See Alcott, B. (2005). “Jevons’ paradox” Ecological Economics 54, no. 1: 9–21.
- See Dimitropoulos, J. (2007). “Energy productivity improvements and the rebound effect: an overview of the state of knowledge.” Energy Policy 35, no. 12: 6354–63.
- I am grateful to Bruce Lankford for helping me clarify this. See Lankford, B. (2013) Resource efficiency complexity and the commons: the paracommons and paradoxes of natural resource losses, wastes and wastages. London: Routledge.
- See Modaresi, R. and D.B. Müller. (2012) “The role of automobiles for the future of aluminum recycling.” Environmental Science & Technology 46, no. 16: 8587–8594.
- OECD (2019), Global material resources outlook to 2060: economic drivers and environmental consequences. Paris: OECD Publishing
- The closest I have come to identifying such a body is the OECD, which has published interesting research on the this subject for a range of materials, but not plastics. OECD (2019), http://www.oecd.org/environment/global-material-resources-outlook-to-2060-9789264307452-en.htm
- The OECD writes that, “Recycling is projected to become more competitive compared to the extraction of primary materials,” but that, “The strong increase in demand for materials implies that both primary and secondary materials use increase at roughly the same speed.” OECD (2019), p. 3
- Most estimates cite to data from the British Petroleum Federation, http://www.bpf.co.uk/press/oil_consumption.aspx
- Energy Information Administration (EIA).2018. “How much oil is used to make plastic?” accessed 1/29/2019 at https://www.eia.gov/tools/faqs/faq.php?id=34&t=6.
- EIA 2018.
- The plastics industry is careful about how it phrases conservation claims in its public relations. It tends to talk about the importance of growing plastics recycling to jobs, litter cleanup, and generally as an end unto itself.
- Geyer, R. et. al. (2017) “Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made.” Science Advances 3, no. 7
- The Plastics Division of the American Chemistry Council (2018). “Life Cycle Impacts of Plastic Packaging Compared To Substitutes in the United States and Canada” accessed 1/29/2019 at https://plastics.americanchemistry.com/Plastic-Packaging-Life-Cycle-Study/
- See Lifset, R.(1995). “Foreward”, in Ince, P. What won’t get harvested, where, and when: the effects of increased paper recycling on timber harvest, Yale University School of Forestry and Environment.
____________________
Samantha McBride is an Assistant Professor at the Baruch College School of Public Affairs and works full time as a professional in urban waste governance in New York City. Her essay was originally published in Discard Studies.
Does recycling actually conserve or preserve things? by Samantha McBrideis licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Adapted from “Chapter 5” of A Guide to Perspective Analysis, 2012, used according to creative commons CC BY-SA 3.0 US.